Disease of the Month – Fabry Disease
Shots:
- Fabry disease is a rare inherited neurological disorder that affects the body's ability to break down lipids into smaller components
- In this reprise of our Disease of the Month report, we bring an illuminating account of Fabry Disease with deep dive analysis of epidemiology, market size, disease management, available therapies, patient advocacy groups, and the key players involved
- For a curated report, reach out to us at connect@pharmashots.com
Fabry disease results from a genetic mutation in the GLA Gene that produces alpha-GAL enzyme which helps break down sphingolipids. The inadequate production of alpha-GAL enzyme leads to the accumulation of fatty substances in the blood vessels. It is an X-linked lysosomal disorder that leads to excessive deposition of neutral glycosphingolipids in the vascular endothelium of several organs and in epithelial and smooth muscle cells. Fabry disease is characterized by the accumulation of a fatty substance in the body, causing symptoms like hand and foot pain and a specific rash, affecting various organs.
Symptoms
Fabry disease affects people differently. A few symptoms may appear in early childhood, and there can be a possibility that symptoms do not appear until later in life. Let’s explore some of the common symptoms of Fabry Diseases
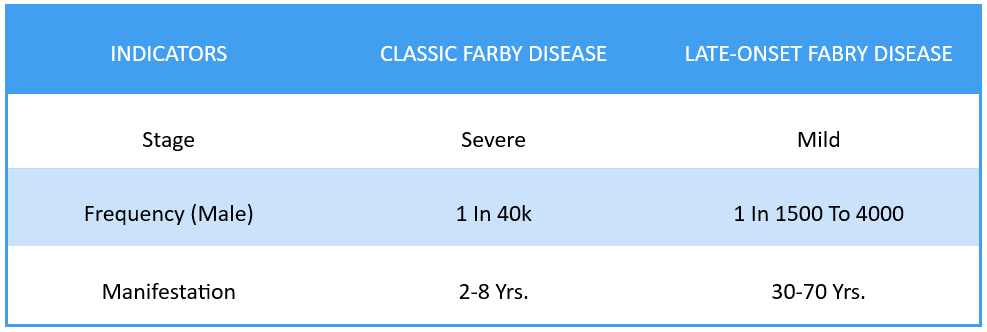
Classic Fabry Disease Symptoms: A typical symptom that may appear in early childhood is the burning sensation in hands and feet. Other symptoms in children include:
- A cluster of dark red spots on skin
- Cloudy eyes
- Gut issues such as constipation and diarrhea
- Difficulty in hearing
Late-Onset Fabry Disease Symptoms: The symptoms in adults do not appear till their 30s. Male patients show severe symptoms vs. Female patients. Some of the common symptoms include:
- Tingling or burning sensation in hands or feet
- Excruciating pain during physical activities
- Intolerance to the heat of the cold
- Abnormal eye pattern
- Dizziness
- Fatigue, fever, and body pain
- Significantly high level of protein in urine
- Hypohidrosis
Causes1
Fabry disease is caused by mutations in the GLA gene, which provides instructions for making an enzyme called alpha-galactosidase A. This enzyme is crucial for the breakdown of GL-3. When the GLA gene is mutated, the enzyme is either absent or non-functional, leading to the accumulation of GL-3 in various tissues and organs.
Diagnosis1,9
Diagnosing Fabry disease involves a combination of clinical evaluation, laboratory tests, and genetic analysis
- Urine Test: A urine test can be used to identify the following biomarkers of Fabry disease:
- Proteinuria (protein in urine) and albuminuria (albumin in urine): Found in the urine suggesting kidney disease due to Fabry disease
- Bikunin levels: Increased bikunin in urine could be a sign of kidney dysfunction in Fabry disease patients
- Mulberry cells: Microscopic examination of these kidney-derived cells that contain accumulated Gb3 can be used to diagnose Fabry disease, including its renal variants
- Urine-derived cell cultures: Urine-derived cells are cultured in the lab to observe the enzymatic activity of alpha-galactosidase A. Can also be utilized to detect mutations in Fabry disease
- Enzyme assay: Measures alpha-GAL enzyme activity in blood
- Genetic Testing: Identifies the GLA gene mutation
- Newborn Screenings: Some states test newborns for Fabry disease and other lysosomal storage disorders
- Tissue Biopsy: Analyzing tissue samples for the presence of GL-3 deposits
- Imaging Studies: MRI or CT scans help assess the extent of organ involvement, particularly in the heart and kidneys
- Cardiac and Renal Function Tests: ECGs and renal function tests evaluate the impact of the disease on these organs
Epidemiology
The frequency of Fabry disease in men is observed to be significantly higher vs. In women as the condition often gets undiagnosed when it comes to women. According to the Orphanet report, the average prevalence of Fabry disease at birth is 1/15,000. Being an underdiagnosed condition, the frequency could be higher.
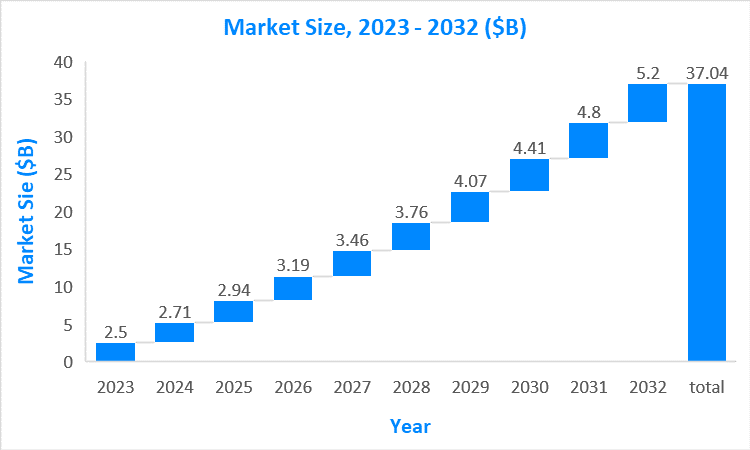
Market Size5
The global Fabry disease market size was valued at $2.5B in 2023 and is forecasted to reach a value of $5.2B by 2032 at a CAGR of 8.5% between 2023 and 2032.
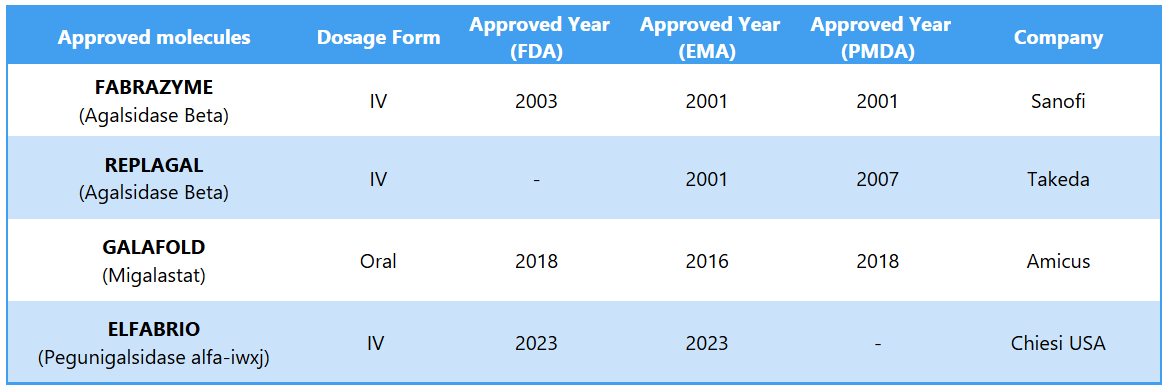
Management and Treatment1,2
Fabry disease has no cure, but pain and gastrointestinal disorders medications can alleviate discomfort. Though there are several treatments available that help reduce fatty accumulation to prevent cardiac and renal issues.
- Enzyme Replacement Therapy (ERT): Administers synthetic alpha-galactosidase A to reduce GL-3 accumulation. Currently available ERTs are FABRAZYME (agalsidase beta) and ELFABRIO (pegunigalsidase alfa)
- Oral Chaperone Therapy: Uses small molecules to stabilize the dysfunctional enzyme. Treatment involves taking GALAFOLD (migalastat) pills on alternate days to repair the damaged alpha-GAL enzyme
- Pain Management: Anticonvulsants and analgesics medications can help manage pain
- Kidney Care: Dialysis or kidney transplantation in advanced cases
- Cardiovascular Care: Medications and interventions to manage heart problems
Product Dashboard6

Key Players in the Market7
Clinical Trial Analysis8
As of Jun 12, 2024, about 80 interventional clinical trials have been registered worldwide for Fabry Disease
Some of the key molecules involved in the trials are- Venglustat (Sanofi), Lucerastat (Idorsia), AL01211 (AceLink Therapeutics), AMT191 (UniQure Biopharma), 4D-310 (4D Molecular Therapeutics), ST-920 (Sangamo Therapeutics)
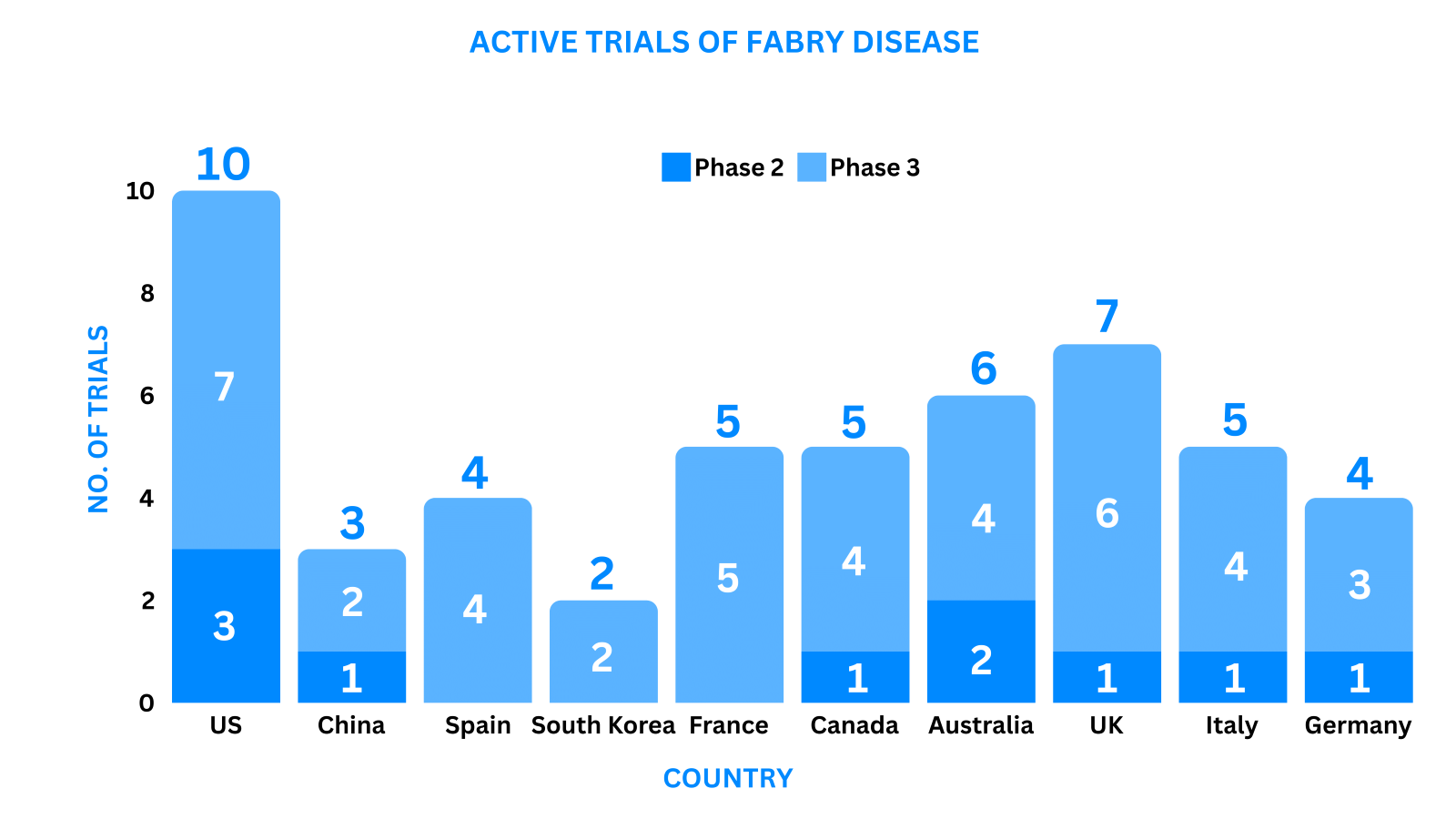
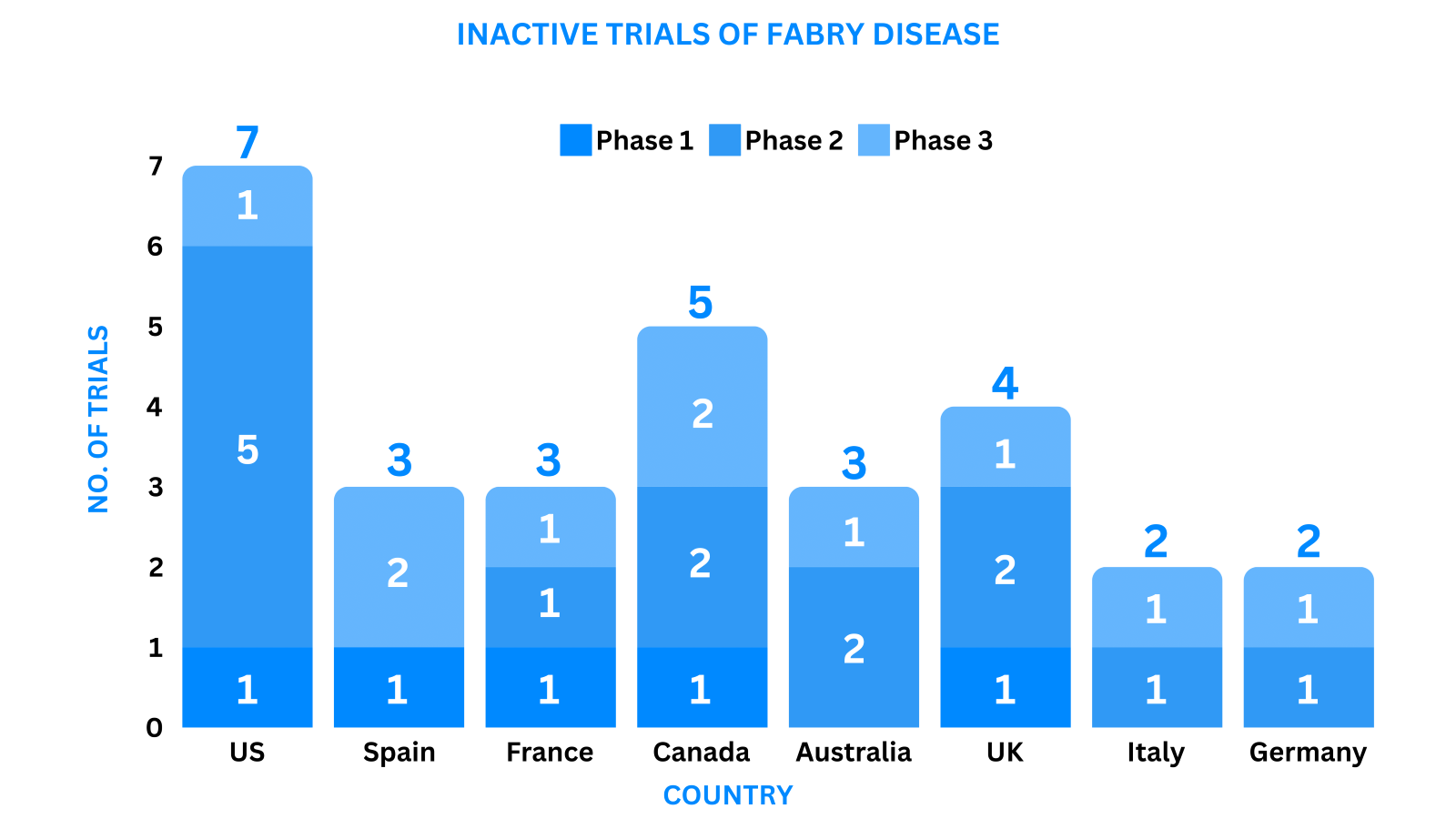
Based on the geographical distribution, the interventional and industry-sponsored clinical trials are classified in the below-mentioned graph into two groups based on their status: Active (recruiting; active, not recruiting; not yet recruiting; enrolling by invitation and suspended) and Inactive (withdrawn; terminated and trials with unknown status)
The maximum number of active trials is being conducted in the US, Australia, UK, Canada, Italy, Germany, Spain, China (as represented in the graph)
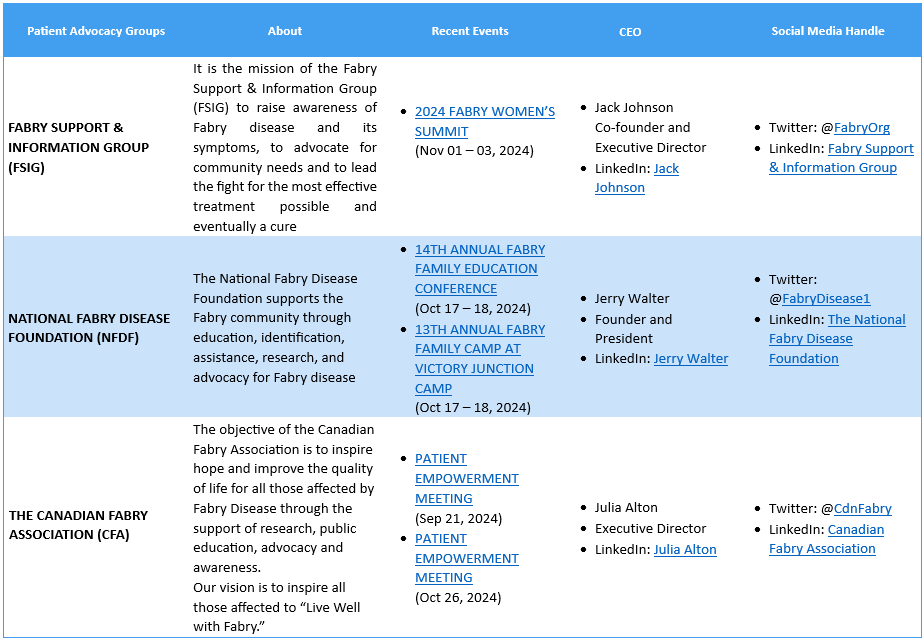
Patient Advocacy Groups (PAGs) for Fabry disease
Patient advocacy for Fabry Disease can be challenging owing to low prevalence, and limited patient care. Though PAGs are dedicatedly working to address the problems of Fabry Disease patients and their families.
References
- Cleveland Clinic
- WebMD
- healthdirect
- Medscape
- Yahoo finance
- GALAFOLD PI
- Fabry Disease News 1
- Clinical Trial
- Fabry Disease News 2
Related Post: Disease of the Month – Sjögren’s Syndrome
Tags

Disha was a content writer at PharmaShots. She is passionate and curious about recent updates and developments in MedTech and Pharma industry. She covers news related to clinical trial results and updates. She can be contacted at connect@pharmashots.com.